On January 28, 2026, the public defense of the doctoral thesis of Maria Zadoń, M.Sc., entitled. “Numerical analysis of tissue heating using combined heat flow and oxygen distribution models”. The dissertation was supervised by Prof. Marek Jasiński, while the reviewers were Prof. Anna Kucaba-Piętal, from Rzeszów University of Technology, Prof. Wiktoria Wojnicz from Gdańsk University of Technology and Prof. Stanisław Kukla from Częstochowa University of Technology.
The Doctoral Committee has approved requests to the Council of the Discipline of Mechanical Engineering to grant Maria Zadoń, M.Sc., the degree of Doctor of Technical Sciences in the discipline of Mechanical Engineering, and to honor his dissertation.
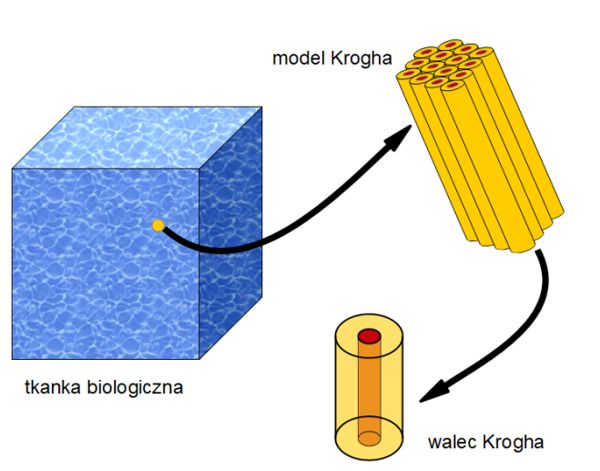
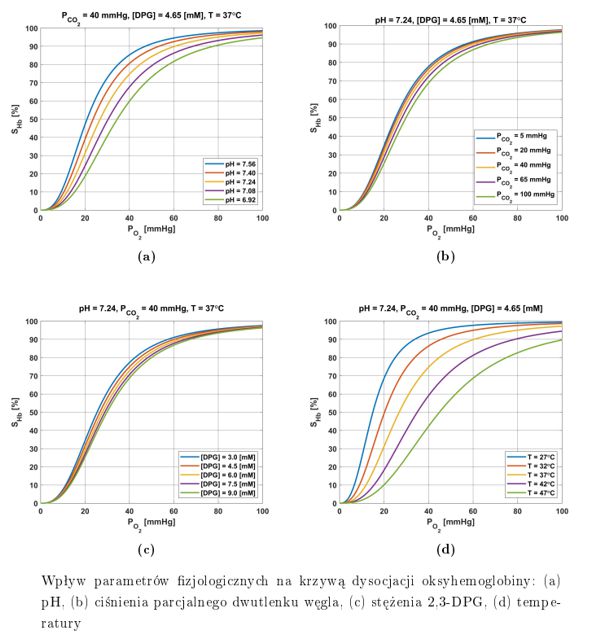
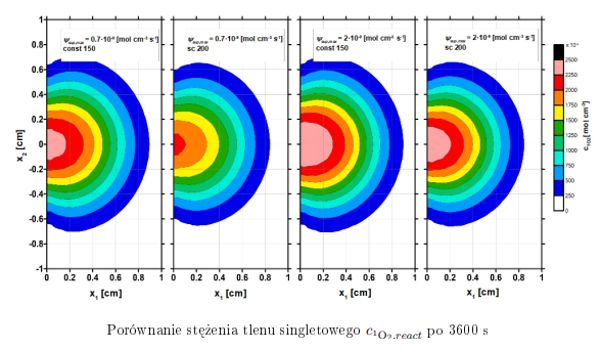
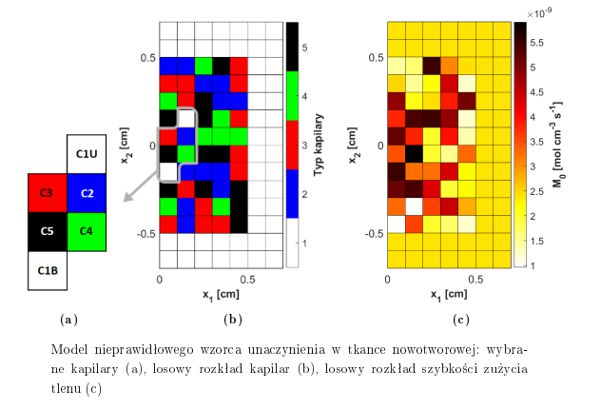
The purpose of the dissertation was to analyze combined models of bioheat transfer and oxygen distribution in tissue subjected to external thermal exposure. For the part related to the temperature field, the Pennes equation and the thermal damage model of the tissue based on the Arrhenius scheme were used. In addition, the variation of the thermophysical parameters of the tissue by temperature and the perfusion coefficient from thermal damage to the tissue were taken into account. A Krogh cylinder described by differential equations for oxygen partial pressure and hemoglobin saturation was used as a model of oxygen distribution, with the equations for the capillary subdomain linked by the corresponding oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve. The combination of models was carried out based on the relationship between the variable perfusion coefficient for the bioheat transfer task and the blood velocity in the capillary, which is a parameter of the oxygen distribution model. The combination of models resulting from the Bohr effect is also included. For the oxygen distribution model, a sensitivity analysis was carried out using the direct method, and the effect of myoglobin and the mitochondrial clustering phenomenon on the occurrence of hypoxia was investigated. A model of photochemical reactions occurring during photodynamic therapy was also considered, which describes the process of generating a cytotoxic form of oxygen as a result of light exposure. Analysis was also made for the reaction model in its combination with the bioheat transfer model, which additionally presents the concept of modeling the tumor region resulting from the irregular vascular within it. A Krogh cylinder was also used to determine the initial concentration of triplet oxygen in the tissue. Since both the bioheat transfer equation and the photochemical reaction model require knowledge of the distribution of light in the tissue, the optical diffusion equation was used, with one variant also accounting for the variation of the effective scattering coefficient from thermal damage to the tissue. In the numerical implementation stage, the finite difference method, the shooting method and the first scheme of the boundary element method were used. In-house algorithms and codes were developed in the MATLAB environment. The final chapter presents conclusions and directions for further research.